Isfahan Mathematics House was established for advancing mathematical sciences.
It is a playground for non-conventional education, an information center for history of mathematics and a place to familiarize young students with various mathematical sciences through observations, collaboration and benefiting from different information resources.
Future Plans
Continuation of previous programs
Creation of a game room
Launching mathematics laboratory
Launching studio for producing the CD for the blinds
Mathematics and the Blinds seminars
Mathematics and Art workshops
Scientific consultations
Producing electronic content
Doing researchers and consultations for industries
Plans about Information Technology:
Teaching Windows and other bases, Internet, Tex, Maple, SAS and other mathematical packages.
Establishment of an interanet as a base for establishment of school – net of Isfahan.
Teaching Logo and other educational softwares to elementary school students.
Establishment of a cafe-net.
Establishment of an Information Club.
Construction of Computer packages for Mathematical Sciences Education.

Proposed projects of Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH) for scientific communication of the sister cities
In order to create contexts for scientific cooperation development between the sister cities of Isfahan, the following recommendations are designed:
1. Information be provided by IMH for sister cities, should be distributed among them
2. Scientific boards will be invited to visit IMH and give lectures in the fields of mathematics, mathematics education and information.
3. Every year math contest is held between teams of students from each city, in IMH
4. Each year, the winners of IMH festivals visit cultural and scientific center of these cities.
5. Collections of textbooks and other publications in the areas of math, science and learning of Mathematics should be prepared for IMH and Subsequently IMH should be ready to provide the same textbooks for those cities. (IMH required these books in order to produce education standards and this opportunity will be extremely valuable.)
6. Young people (pupils and students) from those cities participate in IMH festivals by presenting articles.
7. Possible connection for the students, university students and mathematics teachers, with their colleagues in these cities will be provided via the Internet.
8. Joint Conference on Mathematics education will be organized by the help of math educators from these cities.
9. Joint meeting of specialists in mathematics education of the sister cities will be performed in order to create joint cooperation
10. Attempts will be made to create academic relationships between Isfahan universities and the sister cities’ universities and cooperation agreements will be signed between universities and research institutes with IMH
11. Databases will be shared by the sister cities and Isfahan and also links will be provided with scientific centers of those cities through IMH website.
Isfahan is twinned with:
Lebanon Baalbek, Lebanon[15]
Spain Barcelona, Spain[16]
Nepal Kathmandu, Nepal
Egypt Cairo, Egypt
Senegal Dakar, Senegal
Italy Florence, Italy
Germany Freiburg, Germany
Cuba Havana, Cuba
India Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India
Romania Iaşi, Romania
Turkey Istanbul, Turkey[17][18]
Malaysia Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia[19]
Kuwait Kuwait City, Kuwait
Pakistan Lahore, Pakistan
Russia Saint Petersburg, Russia[20]
Italy Venice, Italy
China Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
Armenia Yerevan, Armenia(1995)[21][22]
Objectives
The Goals of Isfahan Mathematics House are :
- Popularizing mathematics
- Investigating the history of mathematics
- Investigating the applications of mathematics, statistics and computer Sciences
- Developing information technology
- Expanding mathematical sciences among young students
- Promoting team working among young students and teachers
Through :
- Procuring facilities for non-conventional education
- Introducing new instructional techniques
- Establishing Scientific data banks
- Encouraging joint and collaborative research
- Modeling and applying mathematical sciences
- Welcoming relevant novel ideas
Challenging Mathematics – TheMathematics Houses in Iran
This is the appendix of “Les de’fis de I’enseignement des mathe’matiques dans l’education de base” published
by UNESCO, 2011
In this appendix, we briefly present the goals and main activities developed by the Mathematics Houses, a structure created in the last decade in Iran. These perfectly illustrate what can be done in the framework of non-formal education, when the different communities interested in mathematics and mathematics education develop a productive collaboration. As recalled in (Barbeau & Taylor, 2009, p.88), the origin of Mathematics Houses in Iran results from the creation of a high commissionheaded by the President of Iran for the observance of the 2000 World Mathematical Year set up in 1997. This commission indeed took as a goal the creation of Mathematics Houses. The first one opened in Isfahan in 1999. To date mathematics houses exist in Isfahan, Neishabour, Tabariz, Yazd, Kerman, Khomein, Kashmar, Sabzevar, Babul, Zenjan, Gazvin, Gonbad and Najafabad, and a specific
commission has been established for organizing the cooperation between these. Mathematics Houses have six main goals:
- Popularizing mathematics;
- investigating the history of mathematics;
- investigating the applications of mathematics, statistics and computer sciences;
- developing information technology;
- expanding mathematical sciences among young students;
- promoting team working among young students and teachers.
These goals are achieved through:• procuring facilities for non-conventional education;
- introducing new instructional techniques;
- establishing scientific data banks;
- encouraging joint and collaborative research;
- modeling and applying mathematical sciences;
- welcoming relevant novel ideas.
A diversity of activities serving the general public, students of all levels and their families, teachers and even university professors, graduate students, researchers and artists, are organized by the mathematics houses. We list these in the following paragraph, relying on the presentation made in (Barbeau & Taylor, 2009,pp. 88-92) and on a text written by Ali Rejali for the ICMI Bulletin on the occasion of the tenth anniversary of the Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH) (Rejali, 2009). This very active mathematics house is an especially insightful example. More information can be found in its website: www.mathhouse.org
Activities organized by IMH include :
- Lectures (both on popular and special topics in mathematics and mathematicseducation). For instance, every year, there are 5 or 6 public expository lectures and many special talks for special groups of students, teachers and members of the house.
- Mathematics and information technologies exhibitions. Special “days” and “weeks” are regularly organized around such exhibitions. More generally, the mathematics houses provide computer facilities where articipants can use and develop software, access the Internet and benefit from electronic resources for learning mathematics.
- Activities for high school students. These are quite diverse and include research groups which present the results of their investigations in annual festivals or in publications, mathematics team competitions for instance in the frame of the International Tournament of Towns, the Isfahan school net which establishes
electronic communication for schools and provide information technology for education and research, robotics workshops, camps and problem-solving workshops. - Activities for university students: statistics day, research groups involved in collaborative research through electronic communication with Iranian researchers abroad, entepreneurship for giving students the opportunity of designing web pages and software , introductory workshops tothe use of mathematics and statistics
software. - Activities for teachers: research groups invarious educational fields, information technology workshops to train teachers in the use of modern educational devices and familiarize them with information technology, workshops on goals, standards and concepts of mathematics education for elementary teachers, on new secondary courses and information technology for secondary teachers. At IMH, moreover, a group of researchers isdeveloping specific activities for teaching mathematics and computer sciences to blind students. Beyond that IMH and some other mathematics houses maintain specialized libraries providing access to resources of interest regarding mathematics education available in the country. Mathematics houses cooperate between themselves, but they also collaborate with various Iranian institutions such as the Adib Astronomy Centre, the Iranian Mathematical Society, the Iranian Statistical Society, the Isfahan Mathematics Teachers’ Society, the Iranian Association for Mathematics Teachers’ Societies, the Scientific Society for Development of Modern Iran; the Isfahan Society of Moje Nour for the blinds, and the Science and Art Foundation. New forms of cooperation are emerging with some other foreign institutes such as Fontys and the Freudenthal Institute in the Netherlands, or in France the association Animath coordinating the diversity of existing non-formal educational activities in mathematics and the IREM network (Instituts de Recherche sur l’Enseignement des Mathématiques) ) For more information about Animath and non-formal educational activities in mathematics in France, see :(Zehren & Bonneval, 2009). For information about the IREMs, see appendix 9(In no more than one decade, mathematics houses inIran have already achieved a lot, and they are receiving increased international recognition. Zehren, C. & Bonneval, L.M. (Eds.) Dossier: Mathématiques hors classe. Bulletin de
l’APMEP,N° 482, p. 337-403, 2009.
Barbeau E.J., Taylor, P.J. (eds.) Challenging Mathematics In and Beyond the Classroom. The
16th ICMI Study.New York: Springer Science, 2009. 336 p.
Rejali, A. Isfahan Mathematics House. ICMI Bulletin(to appear).
The creation of Isfahan Mathematics House was the result of the hard work of many individuals and associations over a period of almost two decades. As a first result of these efforts, in 1997, Isfahan Teachers Research Centre was established. The principal achievements of this Center were as follows :
- Investigating over the causes of “lack of interest” in mathematics in schools.
- Introducing a model for the formation of the teachers’ educational and scientific societies.
- Encouraging the teachers of different grades to cooperate and share views, along with developing research groups.
These achievements in turn brought about the following consequences :
- Organizing the First Iranian Mathematics Education Conference in 1997.
- Managing mathematics competitions around the country which in turn led to the formation of National Mathematics Olympiad and other scientific Olympiads in the country.
- In 1993, in the 25th Iranian Mathematics Conference held at Sharif University of Technology, the declaration of the year 2000 as the World Mathematics Year by the International Mathematical Union (IMU) was announced. This made two of the active members of the Iranian mathematical community namely Professor Ahmad Birashk (famous Iranian scholar, 1906- 2002) and Dr.Ali Rejali (Chairman of the Scientific Committee of the First Iranian Mathematics Education) put forward a proposal about the formation of a National High Commission of the World Mathematics Year. Soon after, this Commission under the supervision of the President of the Islamic Republic of Iran, approved the formation of Mathematics House project.
- In 1997, within the framework of an agreement signed between Isfahan Municipality and Ministry of Science, Research and Technology, the first Mathematics House was founded in Isfahan. Later on, other Mathematics Houses were founded around the country. Since then, sponsored by Isfahan Municipality, IMH has been considered as one of the leading scientific models in the country, for its activities at local, national & international levels.
The following diagram demonstrates the cooperative participation in the creation of the IMH.
Hossein Shahramnia O( Isfahan Municipality, h.shahram@yahoo.com )
Mohammd Ali Parvanian
Mohammad Alami (Mathematics Teacher )
Forouzan Kheradpajooh(University Professor, kherad_p@cc.iut.ac.ir)
Ali Danaei (University Professor, danaee@shbu.ar.ir)
Ali Zeinal Hamadani ( University Professor, Isfahan University of Technology, hamadani@cc.iut.ac.ir )
Hossein Ali Movahedi (Mathematics Teacher, Ha.movahedi@gmail.com)
Mahmood Khatoon Abadi (University Professor, m.khatoon@yahoo.com)
Mahmoud Talgini (Mathematics Teacher, m_talgini@yahoo.com)
Ali Rejali (University Professor, Isfahan University of Technology, a_rejali@cc.iut.ac.ir)
For the advancement of its goals, Isfahan Mathematics House ( IMH ) has signed mutual cooperation agreements with a number of institutions with similar objectives, inside and outside the country. Some of these institutions are listed below :
- Institute for Studies in Theoretical Physics & Mathematics
- Freudethal Institute
- Science & Arts Foundations
- Fatemi Publishing Company
- Irangate Internet Services
- Fontys Teacher Education Institute
Other cooperating institutions are :
In The Name of God the Compassionate the Merciful
ISFAHAN MATHEMATICS HOUSE (IMH)
CONSTITUTION
CHAPTER ONE
OVERVIEW :
Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH) is established to promote all aspects of mathematics for young people and to prepare them for the fulfillment of cultural and educational goals of our country. The project of its creation was approved by the High Commission of the World Mathematical Year (HCWMY). According to the agreement between the chairmen of the HCWMY and Isfahan Municipality, Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH), is established as a scientific, nongovernmental, nonprofit-making organization under the supervision of the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology with the goals described here below.
ARTICLE 1- Objectives
IMH is established to popularize mathematical knowledge and its applications among people, create an adequate forum for non-classic education, study the history of the Islamic-Iranian scientific heritage, introduce the youth with different mathematical sciences, through observation and cooperation by using different information resources. Other goals of the IMH are studying history of mathematics, development of the information resources and fostering group research activities.
ARTICLE 2
The IMH performs activities on different domains such as scientific, educational, research as well as publications. In addition, the essential performance of the IMH is its concern on non-classic education. Innovations, constructive and fresh thoughts and programs are well acknowledged by the IMH. Devising novel programs such as e-education with the assistance of teachers’ societies and universities are a part of future plans.
ARTICLE 3
IMH is a nonprofit-making institution performing on scientific, educational and research areas as well as publications. It is incorporated and a legal body, its director is considered as its official representative.
ARTICLE 4
The central location of the IMH is Isfahan, Sa’adat Aabad (Aazadgan) Ave. Opposite to Banoo Amins’ Tomb. Local branches of the IMH throughout Isfahan Province may form and start operating, after being approved by IMH Executive and Scientific Committee (ESC) and completion of the official processes.
ARTICLE 5
IMH is a non-political institution; its members are not acting as affiliated of any political party with the name of the IMH.
ARTICLE 6
Since its approval, IMH is created for unlimited time and its members are subject to follow regulations of the country.
CHAPTER TWO
ARTICLE 7
To achieve its goals, as mentioned in article 1, IMH is taking the following measures :
7-1 Creating scientific, research and educational interactions at national and international levels and exchange of viewpoints between teachers, researchers and experts who are involved in the history of mathematics and mathematical sciences and their applications in some way.
7-2 Encouraging teachers, high school and university students to engage them in research and educational tasks related to mathematics.
7-3 Making efforts to promote the scientific levels of school and university students. Acquiring and transferring educational skills through educational workshops at different educational levels.
7-4 Educational planning: Implementing new methods of education, to make it applicable as a tool or a way of thinking to guide students towards the educational goals.
7-5 Conveying scientific experiences, professional development of teachers and creating scientific cooperation platforms.
7-6 Reviewing the school curriculum and presenting proposals for its improvement on qualitative as well as quantitative aspects.
7-7 Creating an interaction bridge between educational centers and teachers of different educational levels to resolve educational problems in mathematics courses as well as connection with other mathematics houses and scientific societies.
7-8 Cooperative activities with Ministry of Education, Ministry of Science, Research and Technology, Ministry of Culture and Islamic Guidance, Tourism and Cultural Heritage Organization, authentic libraries throughout the country, as well as cultural affairs of municipalities and foundations which are involved with mathematics, its history of and education.
7-9 Planning for organizing scientific camps and conferences in order to promote attitude and awareness among the students and teachers.
7-10 Publishing books and scientific journals on mathematics, history of mathematics and astronomy.
7-11 Developing information technology through education, producing materials, e-education and production of scientific educational CD’s.
7-12 Establishing professional libraries and creating interactions with other libraries and information centers.
7-13 Other activities which cover the IMH objectives, if approved by Executive and Scientific Committee (ESC).
CHAPTER 3
MEMBERSHIP
ARTICLE 8
IMH offers different types of membership as described here below :
- Students Membership.
- University Students Membership
- Voluntary Membership
- Institutional Membership
- Honorary Membership
8-1 Student membership: Elementary, intermediate and high school students throughout Isfahan province who are interested in research activities in mathematics are qualified to be IMH members.
8-2 University students’ membership: University students throughout Isfahan who are interested in research activities in different fields of mathematics and development of information technology and communication are qualified to be IMH members.
8-3 Voluntary membership: Individuals who are interested in mathematical sciences and history of mathematics and teachers are qualified to be IMH members after being approved by the ESC.
8-4 honorary membership: scientific figures from inside and outside the country who contribute to the IMH scientifically or financially may join IMH as honorary members after being approved by the ESC.
8-5 institutional membership: institutions that have scientific and research activities related to mathematical sciences and history of mathematics or else support the IMH are eligible to join the IMH.
ARTICLE 9
Each member shall pay an annual due to the IMH as determined by the ESC.
Note 1: The members have no right to claim the membership fees they have paid.
Note 2: Honary members are excluded from paying fees.
CHAPTER FOUR
ARTICLE 10
The organs of the IMH are :
I- Founding Board (FB)
II- Board of Trustees (BT)
III- Executive and Scientific Committee (ESC)
10-1 The duty of the Founding Board, consisting of the following members, is the selection of the BT and the ESC members :
- Yahya Tabesh
- Ali Rejali
- Hoseinali Movahedi
- Ali Hamedani
10-2 The BT is consisting of the following members :
- The Mayor of Isfahan who acts as the director of the BT.
- The representative of the governor of Isfahan province.
- The director of Isfahan Education Department
- The director of Isfahan Management and Programming Organization
- Managing director of the Isfahan Communication Department
- Secretary of Isfahan Mathematics Teachers Society
- One representative appointed by Isfahan University of Technology, Department of Mathematical sciences
- One representative appointed by the University of Isfahan, Mathematics Department
- Seven mathematics figures such as mathematics teachers or faculty members of the universities of Iran as chosen by the BT or the FB in its first term
10-3 Authority and responsibilities of the BT are as follows :
- Setting and approving the general strategies of the IMH as well as considerations thereon
- Approving the IMH budget and submitting corresponding documents to the Municipality of Isfahan and Management and Programming Organization in order to be included in the total budget of the municipality and the province or any other proper authority if needed.
- Studying and approving the balance sheet and annual program
- Studying and approving administrative, financial and organizational as well as interior by-laws and guidelines and principals according to this Constitution.
- Selecting a treasurer and an auditor according to the IMH regulations.
- Selecting the Executive Committee members and affirming the election of the IMH director.
- Revising and modifications in this constitution
10-4 By the call of the director, The Board of Trustees holds meetings twice a year, one in June to approve the balance sheet and the IMH budget amendments and the other in February to approve the programs and the budgets of the following year. In the case of not requesting a meeting by the BT, the ESC will take appropriate measures in this regard, within 10 days.
Note : Other meetings of the BT shall be held by the request of at least 4 members of the BT or the auditor.
10-5 The members of the ESC are :
- The Secretary of Isfahan Mathematics Teachers Society
- Six individuals among mathematics teachers and university faculty members as appointed by the BT
- The director of the IMH, who is the chair of the ESC (after being appointed to this position)
- The Treasurer
10-6 The members of the ESC are elected for a period of two years and may be reelected for a second term
10-7 The meetings of the ESC are held once a month by the call of the director of the IMH
10-8 The meetings of the ESC are held with the presence of all its members and by-laws are approved by a majority of votes
10-9 If a member of the ESC does not attend the meetings three times without permission or if three consecutive times with permission, he or she shall be automatically dismissed. The replacements are made by the BT
10-10 the ESC has complete authority over the scientific and financial affairs of the IMH within the framework of this constitution and the BT by-laws according to the IMH goals
10-11 the duties of the ESC are such cases as :
- Planning for scientific affairs, its development and qualitative promotion
- Planning for activities of different sections of the IMH
- Examining annual budget of the IMH, presented by the director before submitting to the BT for approval
- Examining the balance sheet and annual financial affairs and recommending suggestions to the BT thereon
- Providing the financial By-Laws of the IMH and submitting to the BT as well as supervision thereon
- Forming the organizational chart
- Administrating and protecting the IMH properties and assets
- Supervision over performance of the director
- Determining the amount of salaries of the IMH employees and colleagues and the ways of utilizing the IMH income
- Selecting the IMH director and the auditor and specifying their duties for presenting to the BT
- Specifying the amount of salaries of the director, the auditor and the treasurer and the meetings dues of the members
10-12 the director should have at least a degree of bachelor in mathematical sciences, well-known to the mathematics community. He is appointed by the ESC and approved by the BT
10-13 Authority and responsibilities of the director of the IMH
- Administrating the affairs of the IMH and implementing the ESC resolutions according to the By-laws
- Utilizing the employees effectively and paying their salaries according to the By-Laws
- Representing the IMH for discussions on issues related to the IMH affairs
- Signing contacts with official bodies according to the ESC by-laws
- Creating relationship with corresponding societies and associations
- Formulating necessary decisions for budget planning and administrative by-laws for discussion in ESC and BT meetings
- Appointing and dismissing the staff and granting leave permission and promotion according to the ESC by-laws and within the framework of the regulations
- Signing all financial papers and documents of the IMH
10-14 the ESC may appoint directors for different sections.
10-15 the treasurer: the treasurer appointed by the ESC for a period of 2 years, is responsible to control the financial matters of the IMH and implementing financial resolutions adopted by the ESC. He or she may be reelected for a second term.
10-16 the duties of the treasurer :
- Supervising the budget management
- Controlling the balance sheet and functions made each year for submitting to the auditor
- Controlling the implementation of the by-laws
- Controlling the performance of financial regulations according to the Constitution
- Controlling the expenditure
- Controlling the contracts
10-17 the auditor: The BT selects a deputy for a period of one year as auditor. The auditor may be reappointed. In the first period of its election, the FB is responsible to appoint the auditor.
10-18 the duties of the auditor: the auditor is in charge of controlling the accordance of the administration of the IMH and this constitution and By-laws as well as submitting reports on financial affairs to the BT and the ESC.
ARTICLE 11
The expenditure and possible gifts are registered and reported to the BT after being approved.
ARTICLE 12
All the accounts of the IMH are preserved in Banks as the assets of the IMH.
ARTICLE 13
All relevant documents on financial and non-financial affairs regarding the IMH activities are preserved in the IMH office and shall be presented to related authorities if needed.
ARTICLE 14
In the event of the IMH being dissolved by the BT, the BT shall appoint a committee to discharge the IMH of all its debts. The committee is subject to transfer all the IMH properties and assets to Isfahan Mathematics Teachers Society (IMTS) in Isfahan.
ARTICLE 15
Regarding matters not discussed in this Constitution, the Trade By-Laws are applied.
ARTICLE 16
This Constitution is formulated in four chapters, sixteen articles and three notes.
Fontys Education Institute
Freudenthal Institute
Institute for Studies in Theoretical Physics and Mathematics (IPM)
Interdisciplinary Center for Scientic Computing
Adib Astronomy Center
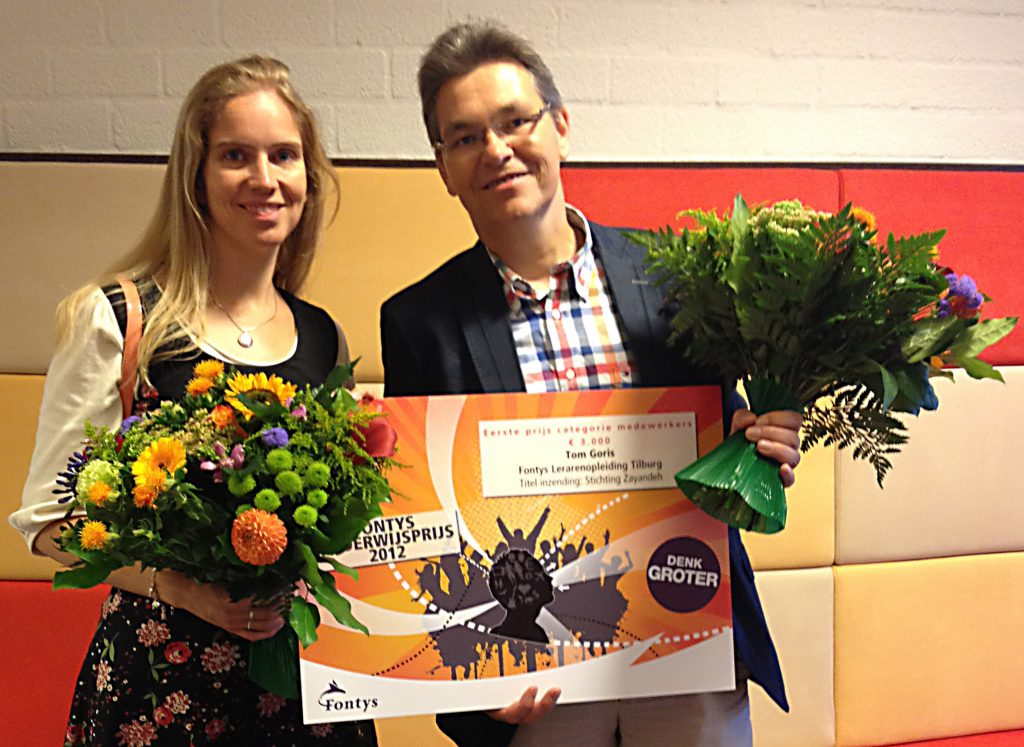
Each year Fontys University of Applied Sciences hands out an award for projects that are initited by its 4000 employees. This projects have to be either international or create a wider perspective to the original discipline or cooperate between several institutes.
The Isfahan Mathematics House has signed a declaration for cooperation with the Fontys Teacher Education Institute in the Netherlands, one of the 31 institutes of Fontys. In order to facilitate this cooperation, Tom Goris and Aldine Aaten founded the Zayandeh Foundation, three years ago.
Out of fifteen proposed projects, the Zayandeh Foundation was unanimously awarded the Fontys Education Prize 2012.
Translation of the jury report:
First prize (€ 3,000) for Tom Goris employee Fontys Teacher Education Institute, Tilburg Supporting letters from :
Harrie Schollen, team leader faculty Mathematics and Economics, Fontys Teacher Education Institute, Tilburg
Bart Habraken, teacher at the Heerbeeck College, Best
Title of the project: Zayandeh Foundation
Motivation :
Together with Aldine Aaten, mathematics teacher at the teacher education institute of the University for applied sciences, Rotterdam, Tom Goris has founded the Zayandeh Foundation in order to initiate and support educational exchange in the field of mathematics between the Netherlands and Iran. This cooperation is a part of the cooperation between the Fontys Teacher Education Institute and the Isfahan Mathematics House, as described in the covenant which both directors signed on October 10th 2007.
The activities of the foundation can be filed into four categories:
Designing and performing workshops in the Netherlands and abroad
Initiating and supporting virtual exchange projects between pupils in the Netherlands and Iran
Exchanging expertise between both countries
Organising excursions to schools for Iranian pupils
The Zayandeh Foundation attempts to create mutual understanding for each other’s culture for young people. This contributes to diminish the prejudices in the western world about Iran and the whole Islamic world. The Foundation keeps the dialogue going in, with approval of both embassies. When politics fail, it is extremely important that projects remain that unites young people.
The jury considers that Tom carries out this international activity with both his professional knowledge and his heart, most of the times not as part of his regular job. Also in his spare time Tom is spending time for (mathematics) education in Iran. It is almost a way of life to support these international exchanges between students of all levels, from primary school kids to college students. With his professional attention Tom took mathematics out of its isolation and created surprising combinations between mathematics and (Islamic) art. This project has a high educational, cultural and social value. The jury has unanimously decided that Tom is the justly winner of the Fontys Education Prize 2012.
Eindhoven, August 27th, 2012
Drs. H. J. T. van de Ven,
Chair of the jury, Fontys Education Prize



WHAT ARE THE MATHEMATICS HOUSES IN IRAN AND WHAT THEY HAVE DONE TO POPULARIZE STATISTICS?
Maryam Ghaemi and Ali Rejali
Isfahan Mathematics House, Iran

Special issue of the journal Olympiad in Informatics
Volume 11 – Special issue (2017)I
Editorial (1-2)I
P.S. KENDEROV
Three Decades of International Informatics Competitions (How did IOI Start?) (3-10)I
Interview with Donald KNUTH
International Olympiad in Informatics: Roads to Algorithmic Thinking (11-20)I
M. GHODSI
Almost Three Decades of IOI in Iran (21-23)I
M.A. ABAM, A. ASADI, A. JABAL AMELI, S.R. SEDDIGHIN, F. SHAHMOHAMMADI
Iranian National Olympiad in Informatics (25-33)I
A. BABAEI, H. ZARRABI-ZADEH, A. SHARIFI-ZARCHI
Kahu and Olympedia: Ideas for Educating Computer Science to High-School Students (35-42)I
H. ZARRABI-ZADEH
Informatics Contests in Iran (43-46)I
H. MIRARMANDEHI, R. MOHAMMADI
Iranian Market for Computer Programmers (47-50)I
G. PIRAYESH, J. ZIARI
Robotics in the Iranian Schools (51-57)I
E. BEHROUZ, M. GHAEMI
Isfahan Mathematics House (59-64)I
Y. TABESH
Computational Thinking: A 21st Century Skill (65-70)I
B. MEHRI
From Al-Khwarizmi to Algorithm (71-74)I
Notes (75-76)

Report on Research Activities of
Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH)
For Promotion of Mathematics Teachers in Primary Schools
Provided and compiled by:
Ali Rejali
(Associate Professor of Isfahan University of Technology and Member of Scientific Board of IMH)
Introduction:
Experiences, class observations in high school classes and studies of members of the committee on primary instruction of Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH) which were carried out by the help of Isfahan Society for Mathematics Teachers (ISMT) and Isfahan Society for Elementary School Teachers (ISEST) show that many teachers are not familiar with the goals of mathematics instruction in primary school. Also, they do not know the weaknesses and defects of these goals and the ways of practicing them in classes. In addition, many teachers are not familiar with mathematical concepts which they teach. In many primary schools, mathematics is not taught properly and many students are just afraid of mathematics because of incorrect instruction methods. These students can not follow and understand new concepts due to the continuity of mathematical concepts and misunderstandings of some basic concepts, in previous schooling

Proceedings of the Seventeenth ICMI Study Conference
“Technology Revisited”
Digital Technology and Mathematics Teaching and Learning; Rethinking the Terrain
Hanoi University of Technology
December 3-8 2006
Edited by Celia Hoyles, Jean-Baptiste Lagrange, Le Hung Son and Nathalie Sinclair
Providing Mathematics e-content
Emran Behrooz
Providing mathematics e-content
Emran Behrooz
Isfahan Mathematics House, and Sepahan Soroosh International IT Training
Corporation (SITCO) IRAN
emran1349@yahoo.com
Mathematics learning seems to be hard and exhausting task for many learners. Mathematics educators and teachers always try to stimulate the public and specially students for studying mathematics. Certainly ICT is an effective tool for providing an interesting atmosphere for mathematics learning. Using this tool, one can make some virtual spaces such as exact diagrams and figures, attractive animations, and most important, making games and parametric programs to provide mutual interactions between learners and teaching media, such that they can change the parameters and see the results in figures or in the processes of the programs and much easier understand the concepts. Isfahan Mathematics House(IMH) was trying to organize content provider teams of these specialists and professionals as its member: Mathematics educator, Mathematicians, Scenarists, Graphic experts and Programmers and multimedia experts. The team was making up some mathematics contents, but it faced to a big problem. It was the lack of communication between these people since many of them don’t understand others with different background. For example the art experts don’t understand mathematics and vice versa. As a solution we tried to train some “interpreters” who can understand or have more feeling of both sides, and finally some successful results raised. In this article we are trying to report these activities with many useful experiences for all interested in the process of providing mathematical e-content.

In the mid 1980s, the International Commission on Mathematical Instruction (ICMI) inaugurated a series of studies in mathematics education by comm- sioning one on the influence of technology and informatics on mathematics and its teaching. These studies are designed to thoroughly explore topics of c- temporary interest, by gathering together a group of experts who prepare a Study Volume that provides a considered assessment of the current state and a guide to further developments. Studies have embraced a range of issues, some central, such as the teaching of algebra, some closely related, such as the impact of history and psychology, and some looking at mathematics education from a particular perspective, such as cultural differences between East and West. These studies have been commissioned at the rate of about one per year. Once the ICMI Executive decides on the topic, one or two chairs are selected and then, in consultation with them, an International Program Committee (IPC) of about 12 experts is formed. The IPC then meets and prepares a Discussion Document that sets forth the issues and invites interested parties to submit papers. These papers are the basis for invitations to a Study Conference, at which the various dimensions of the topic are explored and a book, the Study Volume, is sketched out. The book is then put together in collaboration, mainly using electronic communication. The entire process typically takes about six year.
ICMI STUDY 16
Challenging Mathematics in and beyond the Classroom
Discussion Document
From time to time ICMI (International Commission of Mathematical Instruction) mounts studies to investigate in depth and detail particular fields of interest in mathematics education. This paper is the Discussion Document of the forthcoming ICMI Study 16 Challenging Mathematics in and beyond the Classroom.I
Introduction
Mathematics is engaging, useful, and creative. What can we do to make it accessible to more people?I
Recent attempts to develop students’ mathematical creativity include the use of investigations, problems, reflective logs, and a host of other devices. These can be seen as ways to attract students with material that challenges the mind.I
Initiatives taken around the globe have varied in quality and have met with different degrees of success. New technologies have enabled us to refine our efforts and restructure our goals. It is time to assess what has been done, study conditions for success and determine some approaches for the future.I
Accordingly, ICMI has embarked on its 16th Study, to examine challenging mathematics in and beyond the classroom, and is planning a Conference to be held in Trondheim, Norway, from 27 June to 03 July 2006 at which an invited group of mathematicians and mathematics educators, drawn from around the world, will analyze this issue in detail and produce a report.I
This document will suggest specific issues and invite those who might contribute to the discussion to submit a paper, so that the International Programme Committee can select those attending the Conference.I
Finally, using the contributions to this Conference, a book (the Study Volume) will be produced. This book will reflect the state of the art in providing mathematics challenges in and beyond the classroom and suggest directions for future developments in research and practice.I
The authors of this Discussion Document are the members of the International Programme Committee (IPC) for this ICMI Study. The committee comprises 13 people from different countries, listed at the end of this document. The structure of this Discussion Document is as follows. In section 2 we define and discuss fundamental terms used in the Study. In section 3 we look at the current context, list examples of current practice, observe changes in recent years and identify problems. In section 4 we pose a number of critical questions leading to the results of the Study. In section 5 we call for contributions and outline the process of the Study.I
Description
I(a) Challenge
What is a mathematical challenge? While this may be the topic of discussions during the Study Conference itself, we offer some preliminary thoughts to provide background to debate.I
One answer is that a challenge occurs when people are faced with a problem whose resolution is not apparent and for which there seems to be no standard method of solution. So they are required to engage in some kind of reflection and analysis of the situation, possibly putting together diverse factors. Those meeting challenges have to take the initiative and respond to unforeseen eventualities with flexibility and imagination.I
Note that the word ‘challenge’ denotes a relationship between a question or situation and an individual or a group. Finding the dimensions of a rectangle of given perimeter with greatest area is not a challenge for one familiar with the algorithms of the calculus, or with certain inequalities. But it is a challenge for a student who has come upon such a situation for the first time. A challenge has to be calibrated so that the audience is initially puzzled by it but has the resources to see it through. The analysis of a challenging situation may not necessarily be difficult, but it must be interesting and engaging.I
We have some evidence that the process of bringing structure to a challenge situation can lead one to develop new, more powerful solution methods. One may or may not succeed in meeting a challenge, but the very process of grappling with its difficulties can result in fuller understanding. The presentation of mathematical challenges may provide the opportunity to experience independent discovery, through which one can acquire new insights and a sense of personal power. Thus, teaching through challenges can increase the level of the student’s understanding of and engagement with mathematics.I
We do note that there are several terms used to sometimes describe similar things, but which really have quite distinct meanings. These terms include the expressions ‘challenge’, ‘problem solving’ and ‘enrichment’. We have discussed the term `challenge’ above. Problem solving would appear to refer to methodology, but problem solving is often associated with a challenging situation. Enrichment would be the process of extending one’s mathematical experience beyond the curriculum. This might or might not happen in a challenging context.I
I(b) How do we provide challenges?I
Mathematics can challenge students both inside and outside the classroom. Learning takes place in many contexts. Mathematical circles, clubs, contests, exhibits, recreational materials, or simply conversations with peers can offer opportunities for students to meet challenging situations. It is our responsibility to provide these situations to students, so that they are exposed to challenges both in the classroom and beyond.I
In this endeavour, the role of the teacher is critical. It is the teacher who is faced with the difficult task of keeping alive in the classroom the spontaneity and creativity students may exhibit outside the classroom.I
We note that many teachers do not select problems for lessons on their own, but just follow what is given in a textbook. In this context the role of good textbooks and books of problems is very important. To provide challenge one needs not only to include challenging problems, but also, which is often more helpful, to construct small groups of problems, leading a student from very simple and basic facts and examples to deeper and challenging ones. By carefully selecting problems and organising the structure of textbooks the authors can very much help teachers in providing challenge. It can happen that a student with a good book may develop an interest in the subject even without any help from a teacher.I
The support of the general public is likewise critical. Since children are products of their entire social environment, they need the support of the adults around them in acquiring an understanding and appreciation of mathematics. And, in supporting the new generation, the engagement of citizens in mathematics will open new opportunities for their own personal growth and the public good.I
It is important for us to challenge students of every level of motivation, background or ability. Highly motivated students need challenges so that they don’t turn their active minds away from mathematics and towards endeavours they find more appealing. Mathematical challenges can serve to attract students who come to school with less motivation, and such students learn from challenging material more than they can learn from the mastery of algorithms or routine methods.I
It is particularly important, albeit difficult, to provide challenges for students who struggle to learn mathematics. It is all too easy for students with learning difficulties to content themselves with competence at, or mastery of, algorithmic mathematics, and not attempt to think more deeply about mathematics. However, some practitioners have found that even the learning of routine material is improved when taking place in a challenging environment.I
Particularly valuable are situations that can be used to challenge all students, regardless of their background, or motivational level.I
The process of providing students with challenging situations itself presents challenges for educators. Some of these challenges are mathematical. Teachers must have a wide and deep knowledge of the mathematics they teach, in order to support students who are working on non-standard material. Other challenges to the teacher are pedagogical. In expanding the kinds of experiences students have, teachers must likewise expand their knowledge of student learning, and their ability to interpret what students say. It is the responsibility of the mathematics and mathematics education community to support teachers in these aspects of their growth.I
I(c) Where are Challenges found?I
Challenge situations provide an opportunity to do mathematics, and to think mathematically. Some are similar to the activities of professional mathematicians. These include:I
Solving non-routine problems
Posing problems
Working on problems without achieving a complete solution
Individual investigations
Collaborative investigations in teams
Projects
Historical investigations
Organizing whole-class discussions searching ways to solve a problem, a puzzle or a sophism.I
Other challenges are less like formal mathematics. These attract in a different way, leading into mathematics from other contexts. Some of these are:I
Games
Puzzles
Construction of models
Manipulation of hands-on devices
Still other challenges connect mathematics with other fields. Some examples are:I
Mathematics and other sciences
Mathematics and the humanities
Mathematics and the arts
Real-world problems
Challenges can be found in a variety of venues and vehicles, including:I
Classrooms
Competitions
Mathematics clubs, circles or houses
Independent study
Expository lectures
Books
Papers
Journals
Web sites
Science centres
Exhibits
Festivals, such as mathematics days
Mathematics camps
Current Context
I(a) Practices and Examples
There are many ways that students are currently being challenged. These challenges occur both within and outside of school and include students as well as general members of the public. They can also be classified in several categories such as competitions, problem solving, exhibitions, publications, and what may be roughly called ‘mathematics assemblies’. Below we refer to some particular cases where challenge is organised. To illustrate this we have used examples which are familiar to members of the International Programme Committee.
COMPETITIONS
Exclusive and Inclusive Competitions
There are many well known competitions such as the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) and Le Kangourou des Mathématiques. The former involves small groups of students from many countries (an example of an exclusive competition) while the latter involves thousands of students in France and Europe (an example of an inclusive competition). Details of these and many other competitions can be found on their web sites as well as in the World Federation of National Mathematics Competition’s journal Mathematics Competitions.I
The word ‘competitions’ may initially conjure up an image of rivalry between individual students with ‘winners’ and ‘losers’. While this may be so in certain situations it is not always the case. Even in the IMO, where medals and prestige are at stake, there is more cooperation than rivalry outside the competition room. In all competitions, though, students work ‘against the problem’ as much as they work ‘against each other’ and there are situations where completing the questions is the main aim rather than ‘winning’. And there are competitions where the students have to compose questions for other students to solve rather than having the questions imposed by the competition organizers. Below we give examples of two competitions that are different in some way from the traditional competition where students are essentially submitted to an examination.I
An exclusive competition of interactive style
The competition Euromath is a European cup of mathematics. Each team is composed of 7 people: students from primary school to university and one adult. The six best teams are chosen to participate in the final competition by the results of their work on logical games. In the final, these teams work in front of spectators. To win, a team needs to be quick and to have good mathematical knowledge but the most important thing is ‘l’esprit d’équipe’.I
Another model of an inclusive competition
KappAbel is a Nordic competition for 14 year olds in which whole classes participate as a group. The first two rounds consist of problems distributed on the Internet and downloaded by the teacher. Within a 90 minute time limit, the class discusses the problems and decides how to answer each problem. The third round is divided into two parts: a class project with a given theme (that ends with a report, a presentation and an exhibition), and a problem solving session run as a relay where two boys and two girls represent the class. Recent themes have been Mathematics and local handicraft traditions (2000), Mathematics in games and play (2001), Mathematics and sports (2002), Mathematics and technology (2003) and Mathematics and music (2004). The three best teams from the third round meet on the following day for the final, which is a problem solving session with the teams that did not make it to the final as audience.I
CLASSROOM USE OF CHALLENGE
Problem Solving
The words `problem solving’ have been used to cover a variety of experiences but by the words here we mean allowing students to work on closed questions that they are not immediately able to solve. Hence they need to apply their mathematical content knowledge as well as ingenuity, intuition and a range of metacognitive skills in order to obtain an answer.I
Problem solving is often used in classrooms as a one-off exercise that may or may not be connected to the main mathematical curriculum. It can be seen as a ‘filler’ that many students enjoy but it is not always viewed as central to the mathematics classroom.I
Investigations and projects may be extended problem solving exercises where students look into more difficult problems over more than one period of class time. They frequently involve a written report.I
Teachers who use problems to develop students’ ideas, knowledge and understanding of curriculum material can be considered as taking a `problem solving approach’ to the topic. This approach can reflect the creative nature of mathematics and give students some feel for the way that mathematics is developed by research mathematicians. Examples of both problem solving lessons and lessons which take a problem solving approach can be found on the web site www.nzmaths.co.nz.I
Challenge in traditional education: An example
A traditional method in Japanese elementary school is to solve a problem through full-class discussion. With a skilful teacher, the children can learn more than the curriculum intends. For example, suppose that they are given the problem of dividing 4/5 by 2/3. One student might observe that 6 is the least common multiple of 2 and 3, and write
(4/5)/(2/3)=(4x(6/2))/(5x(6/3))=(4×3)/(5×2)=12/10.
The children can come to realise that this method is equivalent to the standard algorithm and can be used with other choices of fractions. From the teacher’s point of view, this dynamic is unpredictable, and so the teacher requires deep mathematical understanding and sure skills in order to handle the situation. But when the approach succeeds, the children deepen their mathematical experience.I
EXHIBITIONS
Exhibitions, in the sense of gathering material together for people to view or interact with, are becoming increasingly common. These are generally outside of the classroom and may be aimed as much at the general public as they are at students. They can also take place in a variety of settings from schools to museums to shopping malls to the open air. We mention several examples of these.I
The idea of a science centre is to present scientific phenomena in a hands-on way. This means that the visitors are challenged by a real experiment and then try to understand it. Some science centres have mathematical experiments, but there are also science centres devoted exclusively to mathematics, for instance the Mathematikum in Germany or Giardino di Archimede in Italy. These permanent centres, best visited with a guide, attract tens and hundreds of thousands of visitors per year.I
There are also annual exhibitions, varying in content from year to year. An example of this which attracts tens of thousands of visitors per day is Le Salon de la Culture Mathématiques et des Jeux in Paris. Further, there are also occasional exhibitions, such as the international exhibition Experiencing Mathematics sponsored by UNESCO and ICMI jointly with other bodies and presented in 2004 at the European Congress of Mathematics and the 10th International Congress on Mathematical Education.I
Exhibitions can have a special theme, such as the one at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia featuring mathematical machines. These machines are copies of historical instruments that include curve drawing devices, instruments for perspective drawing and instruments for solving problems.I
Instruments for museums, laboratories or mathematics centres may be very expensive. For classroom use small cheaper kits may be available with information about possible classroom use.I
PUBLICATIONS, INCLUDING INTERNET
Publications cover at least books, journals, web sites, CDs, games and software. They are generally accessible to a wide audience.I
School Mathematics Journals
There are many examples around the world of journals designed to stimulate student interest in mathematics. These journals contain historical articles, articles exposing issues with current research, such as the four colour theorem and Fermat’s Last Theorem, and Problem corners, where new problems are posed, other current problems from Olympiads are discussed and students may submit their own solutions. Examples of such journals in the Eastern Bloc, where the traditions are older, are Kömal (Hungary) and Kvant (Russia). In the West outstanding examples are Crux Mathematicorum (Canada), Mathematics Magazine and Mathematical Spectrum (UK).I
Books
There are many publications which enrich and challenge the student’s interest in mathematics. In the English language the Mathematical Association of America has a massive catalogue and the Australian Mathematics Trust has a significant number of publications. In Russian there is also a very rich resource, traditionally published through Mir. In the French language the Kangourou and other publishers have a prodigious catalogue, as does the Chiu Chang Mathematics Education Foundation in the Chinese language. This just refers to major languages. It is expected to be impossible to try to list individual references in this Study. We expect it will be difficult enough to identify the major publishers.I
Internet
There are a number of examples in which people can join a classroom by internet. The ‘e-classroom’ conducted by Noriko Arai is a virtual classroom in which everybody interested in mathematics can join by registration. The classroom is run and supervised by a few mathematicians called moderators. Usually one of them gives a problem such as `’haracterise a fraction which is a finite decimal’. Then, discussions start. A student gives a vague idea to solve the problem, a partial answer or a question, and other students give comments on it or improve former ideas. Moderators encourage the discussions, giving hints if necessary. Usually the discussions end with complete answer. Sometimes a new problem arises from discussions. Otherwise, another problem will be given by a moderator.I
N. Arai developed software so that only students of the classroom can have access to the discussions. In this environment a shy child or an elder person who is not so strong in mathematics may feel more comfortable in joining discussions.I
“MATHEMATICS ASSEMBLIES”
These activities are aimed at groups of people who generally assemble together in one place to be educated by an expert or group of experts. We have in mind here such things as mathematics clubs, mathematics days, summer schools, master classes, mathematics camps, mathematics festivals and so on. Five specific examples are given below that refer to mathematics days, research classes, and industry classes.
School mathematics days
There are many examples around the world of mathematics days in which teams of students from various schools in a district come together. During the day they will participate in various individual and team events in an enjoyable atmosphere, and there may be expository lectures.I
Mathematics Clubs
The world has many examples of mathematics clubs (or circles as they are sometimes known) of students who meet at regular intervals in their town to solve new problems. Often these clubs use a correspondence competition such as the International Mathematics Tournament of Towns as a focus for their activity. These clubs are usually coordinated by local academics, research students or teachers who do so in a voluntary capacity.I
Mathematics Houses
In Iran, a team of teachers and university staff have established what are called Mathematics Houses throughout the country. The Houses are meant to provide opportunities for students and teachers at all levels to experience team work by being involved in a deeper understanding of mathematics through the use of information technology and independent studies. Team competitions, e-competitions, using mathematics in the real world, studies on the history of mathematics, the connections between mathematics and other subjects such as art and science, general expository lectures, exhibitions, workshops, summer camps and annual festivals are some of the non-classic mathematical activities of these Houses.
Research Classes
In Germany for many years the prize for the winners of a mathematical competition is an invitation to a Modellierungswoche. In this, groups of 8 students together with two teachers work on a real application problem posed by local industry. Many of the problems are optimisation problems. The solution normally requires modelling, mathematical analysis and making a computer program.I
As another example, in Math en jeans each team works in collaboration with a university researcher who has propoed a problem, ideally connected to his/her research, on which the students work for a long period (often up to a full school year).I
(b) Trends
It seems that, with few exceptions, the overall trends are positive. For example, there are many new competitions that cater for a wider range of students than the more traditional Olympiad-style conpetition and include younger children than before. Many competitions now involve groups of students rather than just individuals.I
In recent years too, problem solving has been added to the curricula of a number of countries. However, without some professional development for teachers, it may not appear in the actual curriculum delivered in class.I
In the same vein, there appears to be an increasing number of mathematical exhibitions. For a while, mathematical exhibits generally appeared in science centres but now there are more exhibitions devoted solely to mathematics. And, instead of being held in museum-like settings, mathematics exhibitions exist that are portable or appear in such unusual settings as shopping centres, subways, and the open air.I
As for publications, there recently seems to have been an increasing number of books and films of a mathematical nature for the general public. Some of these, such as Fermat’s Last Theorem and A Beautiful Mind, have been extremely successful. On the book side though, there may be a trend away from classical problem books to books that discuss mathematical topics and are meant to be read rather than worked on. These books may attempt to convey deep and complicated mathematics but they do so by creating an impression rather than going into great details.I
In recent years the Moscow Centre for Continuous Mathematical Education has published a series of books The library of mathematical education. These are small books (20-30 pages) written by professional mathematicians and addressed to interested high school students. They include popular explanations of various areas of mathematics, challenging problems for students and history. The small size of the volumes, good illustrations, and popular style of writing attract a lot of readers.I
It appears that magazines and newspapers are currently carrying more mathematics, both with stories about contemporary mathematics and with problems or puzzles.I
Mathematics can be found in many sites on the internet. These sites range from discussions of specific topics to problem sites, to the history of mathematics, to teacher professional development, to games (including sites that claim to read your mind), to emergency rooms where you can ask for mathematical help. There are even more and varied sites that all help to make mathematics more accessible, if not popular.I
I(c) Problems Identified
The difficulties that these contexts produce fall into two categories: development and applications. In the former category most new initiatives depend on a small number of people for their success. This makes them fragile. It seems often easier to find money to begin new projects than to find continuing support for them.I
By applications we mean applications in schools. It is not clear that much of the new material available is being used successfully by great numbers of teachers in the regular classroom. This may be for a variety of reasons. First, teachers are frequently plagued with time constraints as more material, especially involving new subjects outside of mathematics, enters the school curriculum. These subjects reduce the time available for mathematics. Second, especially in senior secondary school, high stakes examinations force teachers into teaching for the examination rather than developing mathematical ideas. And third, teachers may lack the confidence to deal with the new material that was not part of their undergraduate training. They may also be uncomfortable with the more open pedagogy required for challenging situations which are, by their nature, less structured than the traditional pedagogy.I
Questions Arising
One goal for the Study Conference will be to get a good picture of what is the state of the art. Here are some examples of issues that may be considered in the context of this Study.I
Impact of teaching and learning in the classroom:I
How do challenges contribute to the learning process?I
How can challenges be used in the classroom?I
How much challenge is provided in current curricula?I
What further opportunities to challenge would enhance teaching and learning in the regular classroom?I
How can teachers be made aware of the existence of the different types of challenges?I
How can we ensure that these challenges are compatible with the mandated syllabus?I
How can time constraints in the classroom be handled?I
How can challenges be evaluated?I
How can students be evaluated in challenges?I
How can the effectiveness of using challenging materials be supported by the grading system?I
What sorts of challenges are appropriate for remedial and struggling students?I
What are the implications for teacher training of challenges which are in the classroom?I
What are the implications for teacher training for challenges which exist outside of the classroom?I
What background do students need to handle challenge material and how can this be introduced into the classroom? This includes familiarity with mathematical notation and conventions, ability to reason and draw conclusions, ability to observe and classify and skill at communication.I
How can ‘beyond classroom activities’ like competitions, exhibitions, clubs, maths fairs etc influence the classroom activities and learning in such a way that all students in the class are challenged and motivated?I
How can teachers, parents and students be made aware that these kinds of activities and challenges also will strengthen the learning and understanding of basic concepts and skills in mathematics?I
Can experience with competitions, maths fairs etc be part of teacher training and in service teacher education? And will this help to engage teachers in `beyond classroom activities’ or implement these kinds of activities in classroom practice?I
How can textbooks be written so that challenging activities is the philosophy and leading idea behind the textbook, and not only fragmental parts of the content of the book?I
How can technology be used by teachers and students to create challenging environments?I
Beyond classroom activities
What is the effect on the visitors of exhibitions, festivals etc where they have only a short meeting with mathematical challenges? How can parents, teachers, students and others be helped to go deeper into the mathematics beyond these short meetings?I
How can one make visible the mathematics behind everyday technological devices, and how can this be put into a context that is accessible and mathematically challenging for different groups of people?I
Research
What research has been done to evaluate the role of challenge?I
What can research into the use of challenge tell us about the teaching and learning of mathematics?I
What questions require further research?I
More general questions
How can the mathematics and mathematics education community be involved in this kind of challenging activity that goes beyond their own research interests?I
Are there some branches of mathematics that are more suitable for producing challenging problems and situations?I
How can different designs of challenging activities, in particular competitions, attract different groups of people (the very able students, gender, cultural differences, different achievement etc)
What can be done to identify, stimulate and encourage the mathematically talented students?I
Call for Contributions
The work of this Study will take place in two parts. The first consists of a Conference to take place in Trondheim, Norway, from 27 June to 03 July 2006. The Conference will be a working one. Every participant will be expected to be active. Participation is by invitation only, based on a submitted contribution. Among the attendees, it is planned to represent a diversity of expertise, experience, nationality and philosophy. Such attendance should be drawn broadly from the mathematics and mathematics education community. It is hoped that the Conference will attract not only long term workers in the field but also newcomers with interesting and refreshing ideas or promising work in progress. In the past, ICMI Study Conferences have included about 80 participants.I
The IPC hereby invites individuals or groups to submit contributions on specific questions, problems or issues related to the theme of the Study for consideration by the Committee. Those who would like to participate should prepare
(a) a one-page listing of their current position and contact information, as well as of their past and present publications and activities pertinent to the theme of the Study;I
(b) a paper of 6-10 pages addressing matters raised in this document or other issues related to the theme of the Study.I
Proposals for research that is on its way, or still to be carried out, are also welcome. Research questions should be carefully stated and a sketch of the outcome – actual or hoped for – should be presented, if possible with reference to earlier and related studies.I
These documents should be submitted no later than August 31, 2005, to both co-chairs of the Study either by post, by facsimile or (preferably) by e-mail. All such documents will be regarded as input to the planning of the Study Conference and will assist the IPC in issuing invitations no later than January 31, 2006. All submissions must be in English, the language of the Conference.I
The contributions of those invited to the Conference will be made available to other participants beforehand as preparation material. Participants should not expect to present their papers orally at the Conference, as the IPC may decide to organize it in other ways that facilitate the Study’s effectiveness and productivity.I
Unfortunately an invitation to participate in the Conference does not imply financial support from the organizers, and participants should finance their own attendance at the Conference. Funds are being sought to provide partial support to enable participants from non-affluent countries to attend the Conference, but the number of such grants will be limited.I
The second part of the Study is a publication which will appear in the ICMI Study Series. This Study Volume will be based on selected contributions submitted as well as on the outcomes of the Conference. The exact format of the Study Volume has not yet been decided but it is expected to be an edited coherent book which it is hoped will be a standard reference in the field for some time.I
International Programme Committee
Co-chair: Edward J. Barbeau
University of Toronto, CANADA
Co-chair: Peter J. Taylor
University of Canberra, AUSTRALIA
Chair, Local Organising Committee: Ingvill M. Stedøy
Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, NORWAY
Mariolina Bartolini Bussi
University di Modena et Reggio Emilia, ITALY
Albrecht Beutelspacher
Mathematisches Institut, Gie\ss en, GERMANY
Patricia Fauring
Buenos Aires, ARGENTINA
Derek Holton
University of Otago, Dunedin, NEW ZEALAND
Martine Janvier
IREM, Le Mans, FRANCE
Vladimir Protasov
Moscow State University, RUSSIA
Ali Rejali
Isfahan University of Technology, IRAN
Mark E. Saul
Gateway Institute, City University of New York, USA
Kenji Ueno
Kyoto University, JAPAN
Bernard R. Hodgson, Secretary-General of ICMI
Université Laval, Québec, CANADA
Advisors from ICMI Executive Committee
Maria Falk de Losada
University Antonio Narino, Bogota, COLOMBIA
Petar Kenderov
Academy of Sciences, Sofia, BULGARIA
Inquiries
Inquiries on all aspects of the Study, suggestions concerning the content of the Study Conference and submission of contributions should be sent to both co-chairs:
Prof. Edward J. Barbeau
Department of Mathematics
University of Toronto
Toronto M5S 3G3
CANADA
Tel: +1 416 653 1961
Fax: +1 416 978 4107
E-mail: barbeau@math.toronto.edu
Prof. Peter J. Taylor
Australian Mathematics Trust
University of Canberra ACT 2601
AUSTRALIA
Isfahan Mathematics House in French Maths Commission

Impressions of Iran
The stakes of education, teachers and houses of mathematics
Invitation by Farhangian University (in charge, at the national level of teacher training):
Opportunity to discover a very active “mathematical education” community …
Isfahan House of Mathematics
Education has a main role in the sustainable development of a country; because one can consider it as a factory in which human beings are the products, but unfortunately this important role in not recognized by many countries [1]. On the other hand, the teachers are the most important part of the education system, which are not only at the end of the process for just teaching the students, but they must have major roles in curriculum development and evaluation process of education by being involved in making the standards, developing frameworks, writing text books and providing resources and even evaluating the system of education. In many countries there are special universities or training centres for educating the teachers, but are their programs sufficient to fulfil all of the requirements for being a teacher? We also have in service programs all over the world, but are all these programs designed well? It is obvious that a teacher must obtain some kind of teacher certificate before starting to teach at school and only graduation from such institutes is not enough. Isfahan Mathematics house (IMH) believes that the teachers must have group discussions among themselves in each school, in each region and at national and international levels, possibly via scientific societies and scientific meetings, so that they can play their role properly. They should write down their experiences for making resources not only for their Colleagues, but also for education researchers, as well. IMH as an NGO (non-government-organization), which established by mathematics teachers in schools and universities during its life time (since 1999) tries to organize such communities for primary school teachers intermediate school teachers and high school teachers and even the university lecturers [2,3] Also there exists a research group in the house consists of economists, educators and teachers who work on the idea of how one can help the decision makers to think at education as the most important productive tool, and not as a service work of the government. They have gathered information from many developed countries, which respect education and the teachers have well prestige. Mission Statement of the house is that Mathematics House is a lively and creative research centre with the following goals: giving all members of the society the power of having an improved quality personal and social life; developing mathematical Awareness among the society; sing mathematical sciences in all aspects of life and ork; encouraging team working; encouraging Interdisciplinary Research; emphasis on incident learning ;teaching the skills for a better understanding of athematics concepts; teaching the skills for solving (real ife, mathematical, scientific) and social problems by using athematical concepts and methods.In Report on Visit in Iran from August 23 to September 6,2003, Professor Michel Waldschmidt, the President of the French Mathematical Society, mentions that “The Mathematics Houses deserve some comments. In France we have two scientific museums in Paris (Palais de la Découverte, the older one, and Musée des Sciences de la Villette, a more recent one), but there is nothing like the Math Houses outside Paris. I believe that these houses will contribute to attract young schoolboy and schoolgirls to pursue scientific studies. This is extremely important for the future of a country, including technological development, and Iran may avoid the rather bad situation that many developed countries are facing, where not enough young students are attracted by science”. Also Professor Jan Hogendijk, professor of history of mathematics at Utrecht University, in an article wrote that: “A more modern secret in Isfahan is its House of Mathematics, which encourages mathematics awareness among high school teachers and university students work together with high school projects. The circumstances are sometimes difficult but this only seems to make the staff more enthusiastic and more inventive. Dutch mathematics educators can learn a lot in Iran and formal cooperation agreements have been made between the House of Mathematics, the Freudenthal Institute at the University of Utrecht and Fontys teacher training college in Eindhoven. Our group of students was received warmly by the staff, who organized most of our scientific program in Iran”[4]. Also in an speech at the 10th anniversary of the house he said: ” The House of mathematics exists in Isfahan, which is not an arbitrary city, but the city with the most beautiful Islamic tilings (kashikariha) in the world. This is to my mind, a coincidence because the House of Mathematics was not founded because of the Islamic tiling. But it is a wonderful coincidence. The kashikariha in, for example, Masjid-e Jom’eh and Darb-i Imam are not only beautiful; they also involve deep mathematics. The tilings of Isfahan are much more interesting than, for example, the famous tilings in the Alhambra in Spain. Unfortunately, many people in today’s world hate mathematics. But almost everybody likes the kashikariha of Isfahan. Thus, these kashikariha can be used to introduce mathematics to people. This is one of the things which the House of Mathematics is trying to do, and we hope that this will eventually develop into a large project on an international scale, with a substantial impact on mathematics education.”I
Ali Rejali & Foroozan Kheradpazhuh
Fondateur et directeur de la MM
Références
[1] Rejali, A., & Hematipour, N. (2013). Challenging Mathematics through the Improvement of Education, Mathematics Competitions, 2013 Vol. 26 No. 2, pp. 34-41
[2] Barbeau, E.J., Taylor, P. J. (Eds.) (2009). Challenging Mathematics In and Beyond the Classroom, the 16th ICMI Study, New ICMI Study Series, 2009
[3] Mathematics Houses in Iran (2012). In Challenging Mathematics in Basic Mathematics Education. Annex 10, pp 84-87. UNESCO
[4] Hogendijk, J. (2008). Ancient and modern secrets of Isfahan, Nieuw Archief voor Wiskunde, fifth series, 9; p. 121

Challenging Mathematics – The Mathematics Houses in Iran
Appendix 10 : Challenging Mathematics – The Mathematics Houses in Iran
This is the appendix of
“Les de’fis de I’enseignement des mathe’matiques dans l’education de base”
Published by UNESCO, 2011
In this appendix, we briefly present the goals and main activities developed by the Mathematics Houses, a structure created in the last decade in Iran. These perfectly illustrate what can be done in the framework of non-formal education, when the different communities interested in mathematics and mathematics education develop a productive collaboration.
As recalled in (Barbeau & Taylor, 2009, p.88), the origin of Mathematics Houses in Iran results from the creation of a high commission headed by the President of Iran for the observance of the 2000 World Mathematical Year set up in 1997. This commission indeed took as a goal the creation of Mathematics Houses. The first one opened in Isfahan in 1999. To date mathematics houses exist in Isfahan, Neishabour, Tabariz, Yazd, Kerman, Khomein, Kashmar, Sabzevar, Babul, Zenjan, Gazvin, Gonbad and Najafabad, and a specific commission has been established for organizing the cooperation between these.
Mathematics Houses have six main goals:
1. popularizing mathematics;
2. investigating the history of mathematics;
3. investigating the applications of mathematics, statistics and computer sciences;
4. developing information technology;
5. expanding mathematical sciences among young students;
6. promoting team working among young students and teachers.
These goals are achieved through:
- procuring facilities for non-conventional education;
- introducing new instructional techniques;
- establishing scientific data banks;
- encouraging joint and collaborative research;
- modeling and applying mathematical sciences;
- welcoming relevant novel ideas.
A diversity of activities serving the general public, students of all levels and their families, teachers and even university professors, graduate students, researchers and artists, are organized by the mathematics houses. We list these in the following paragraph, relying on the presentation made in (Barbeau & Taylor, 2009, pp. 88-92) and on a text written by Ali Rejali for the ICMI Bulletin on the occasion of the tenth anniversary of the Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH) (Rejali, 2009). This very active mathematics house is an especially insightful example. More information can be found in its website: www.mathhouse.org
Activities organized by IMH include:
1- Lectures (both on popular and special topics in mathematics and mathematics education). For instance, every year, there are 5 or 6 public expository lectures and many special talks for special groups of students, teachers and members of the house.
2- Mathematics and information technologies exhibitions. Special “days” and “weeks” are regularly organized around such exhibitions. More generally, the mathematics houses provide computer facilities where participants can use and develop software, access the Internet and benefit from electronic resources for learning mathematics.
3- Activities for high school students. These are quite diverse and include research groups which present the results of their investigations in annual festivals or in publications, mathematics team competitions for instance in the frame of the International Tournament of Towns, the Isfahan school net which establishes electronic communication for schools and provide information technology for education and research, robotics workshops, camps and problem-solving workshops.
4- Activities for university students: statistics day, research groups involved in collaborative research through electronic communication with Iranian researchers abroad, entepreneurship for giving students the opportunity of designing web pages and software , introductory workshops to the use of mathematics and statistics software.
5- Activities for teachers: research groups in various educational fields, information technology workshops to train teachers in the use of modern educational devices and familiarize them with information technology, workshops on goals, standards and concepts of mathematics education for elementary teachers, on new secondary courses and information technology for secondary teachers.
At IMH, moreover, a group of researchers is developing specific activities for teaching mathematics and computer sciences to blind students. Beyond that IMH and some other mathematics houses maintain specialized libraries providing access to resources of interest regarding mathematics education available in the country. Mathematics houses cooperate between themselves, but they also collaborate with various Iranian institutions such as the Adib Astronomy Centre, the Iranian Mathematical Society, the Iranian Statistical Society, the Isfahan Mathematics Teachers’ Society, the Iranian Association for Mathematics Teachers’ Societies, the Scientific Society for Development of Modern Iran; the Isfahan Society of Moje Nour for the blinds, and the Science and Art Foundation. New forms of cooperation are emerging with some other foreign institutes such as Fontys and the Freudenthal Institute in the Netherlands, or in France the association Animath coordinating the diversity of existing non-formal educational activities in mathematics and the IREM network (Instituts de Recherche sur l’Enseignement des Mathématiques) (For more information about Animath and non-formal educational activities in mathematics in France, see (Zehren & Bonneval, 2009). For information about the IREMs, see appendix 9.)
In no more than one decade, mathematics houses in Iran have already achieved a lot, and they are receiving increased international recognition.
- Zehren, C. & Bonneval, L.M. (Eds.) Dossier : Mathématiques hors classe. Bulletin de l’APMEP, N° 482, p. 337-403, 2009.
- Barbeau E.J., Taylor, P.J. (eds.) Challenging Mathematics In and Beyond the Classroom. The 16th ICMI Study. New York: Springer Science, 2009. 336 p.
- Rejali, A. Isfahan Mathematics House. ICMI Bulletin (to appear).
As recalled in the 16th Study of ICMI, the origin of Mathematics Houses in Iran results from the creation of a high commission for the observance of the 2000-World Mathematical Year, set up in 1997 (Taylor & Barbeau, 2009). This commission took as a goal, the creation of Mathematics Houses. The first one opened in Isfahan in 1999, with the help of the municipality of Isfahan. The Houses are meant to provide opportunities for executing diversity of activities serving the general public, students at all levels and their families, teachers, university students, researchers and even university professors. Mathematics House is a lively and creative research center with the following goals; popularizing mathematics, developing mathematical awareness among the society, using mathematical sciences in all aspects of life and work, encouraging team working, promoting team working among young students and teachers, encouraging joint and collaborative research, encouraging interdisciplinary research, emphasis on incident learning, teaching the skills for a better understanding of mathematical concepts, teaching the skills for solving problems by using mathematical concepts and methods, investigating the history of mathematics, investigating the applications of mathematics, statistics and computer Sciences, developing information technology and expanding mathematical sciences among young students (Challenging Mathematics, 2012). Professor Jan Hogendijk, professor of the history of mathematics at Utrecht University in an article wrote that, “A more modern secret in Isfahan is its House of Mathematics, which encourages mathematics awareness among high school teachers and university students work together with high school projects. The circumstances are sometimes difficult but this only seems to make the staff more enthusiastic and more inventive” (Hogendijk, 2008). Now, there are 45 Mathematics Houses throughout the country and two others in France and Belgium. In ICME-13 in Germany, an International Network of Mathematical Houses was established (Kaiser, 2016).
The first mathematics house established in Isfahan (Iran) through the cooperation of some Iranian school teachers and university faculties since 1999 (Barbeau et. al., 2009).
Currently, there are more than 30 mathematics houses across the country and also more mathematics houses have established in France, Belgium and etc. Recently an international network of Mathematics Houses has been organized at the 13th International Congress of Mathematics Education in Germany in 2016 to foster more international collaboration.
Mathematics House is an innovative learning center focused on mathematics and informatics education but in a non-curricular way. It is a place for experimental learning
through workshops and projects, and subsequent reflection in showcases and mathematics festivals. One prominent example is Isfahan Mathematics House, a center of excellence as a learning environment (Barbeau et. al., 2009, Challenging Mathematics UNESCO, 2012)
Mathematics Houses have six main goals:
1. popularizing mathematics;
2. investigating the history of mathematics;
3. investigating the applications of mathematics, statistics and computer sciences;
4. developing information technology;
5. expanding mathematical sciences among young students;
6. promoting team working among young students and teachers.
These goals are achieved through:
• procuring facilities for non-conventional education;
• introducing new instructional techniques;
• establishing scientific data banks;
• encouraging joint and collaborative research;
• modeling and applying mathematical sciences;
• welcoming relevant novel ideas.
A diversity of activities serving the general public, students of all levels and their families, teachers and even university professors, graduate students, researchers and artists, are organized by the mathematics houses. We list these in the following paragraph, relying on the presentation made in (Barbeau & Taylor, 2009, pp. 88-92) and on a text written by Ali Rejali for the ICMI Bulletin on the occasion of the tenth anniversary of the Isfahan Mathematics House (IMH) (Rejali, 2009). This very active mathematics house is an especially insightful example.
Activities organized by IMH include:
1- Lectures (both on popular and special topics in mathematics and mathematics education). For instance, every year, there are 5 or 6 public expository lectures and many special talks for special groups of students, teachers and members of the house.
2- Mathematics and information technologies exhibitions. Special “days” and “weeks” are regularly organized around such exhibitions. More generally, the mathematics houses provide computer facilities where participants can use and develop software, access the Internet and benefit from electronic resources for learning mathematics.
3- Activities for high school students. These are quite diverse and include research groups which present the results of their investigations in annual festivals or in publications, mathematics team competitions for instance in the frame of the International Tournament of Towns, the Isfahan school net which establishes
electronic communication for schools and provide information technology for education and research, robotics workshops, camps and problem-solving workshops.
4- Activities for university students: statistics day, research groups involved in collaborative research through electronic communication with Iranian researchers
abroad, entepreneurship for giving students the opportunity of designing web pages and software , introductory workshops to the use of mathematics and statistics
software.
5- Activities for teachers: research groups in various educational fields, information technology workshops to train teachers in the use of modern educational devices and
familiarize them with information technology, workshops on goals, standards and concepts of mathematics education for elementary teachers, on new secondary
courses and information technology for secondary teachers.
At IMH, moreover, a group of researchers is developing specific activities for teaching mathematics and computer sciences to blind students. Beyond that IMH and some other mathematics houses maintain specialized libraries providing access to resources of interest regarding mathematics education available in the country.
Mathematics houses cooperate between themselves, but they also collaborate with various Iranian institutions such as the Adib Astronomy Centre, the Iranian Mathematical Society, the Iranian Statistical Society, the Isfahan Mathematics Teachers’ Society, the Iranian Association for Mathematics Teachers’ Societies, the Scientific Society for Development of Modern Iran; the Isfahan Society of Moje Nour for the blinds, and the Science and Art Foundation. New forms of cooperation are emerging with some other foreign institutes such as Fontys and the Freudenthal Institute in the Netherlands, or in France the association Animath coordinating the diversity of existing non-formal educational activities in mathematics and the IREM network (Instituts de Recherche sur l’Enseignement des Mathématiques)
.
